Hijab
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
For the municipal company of Gothenburg, Sweden, see Higab.
Women wearing hijab
 |
| Part of a series on |
| Islamic culture |
|---|
| Architecture |
| Art |
| Dress |
| Holidays |
| Literature |
| Music |
| Theatre |
Most often, it is worn by Muslim women as a symbol of modesty, privacy and morality. According to the Encyclopedia of Islam and Muslim World, modesty in the Quran concerns both men's and women's "gaze, gait, garments, and genitalia."[6] The Qur'an admonishes Muslim women to dress modestly and cover their breasts and genitals, but it doesn't require covering the head.[7] Most Islamic legal systems define this type of modest dressing as covering everything except the face and hands in public.[5][8] These guidelines (for covering of the entire body except for the hands, the feet and the face) are found in texts of fiqh and hadith developed after the revelation of the Qur'an but, according to some, are derived from the verses (ayahs) referencing hijab in the Qur'an.[6] Many believe that the Qur'an itself does not mandate that women wear hijab.[9][10]
The term hijab in Arabic literally means “a screen or curtain” and is used in the Qur'an to refer to a partition. The Qur'an tells the male believers (Muslims) to talk to the wives of Muhammad behind a curtain. This curtain was the responsibility of the men and not the wives of Muhammad. This leads some to claim that the mandate of the Qur'an to wear hijab applies to the wives of Muhammad, not women generally.[11][12] Αlthough hijab is often seen by critics as a tool utilized by men to control and silence women, the practice is understood differently in different contexts.[13]
Contents
In Islamic texts
Quran
The Quran instructs both Muslim men and women to dress in a modest way, but it doesn't insist on covering the head:"Tell the believing men to lower their gaze and be modest" (surah 24:30)
The clearest verse on the requirement of the hijab is surah 24:30–31, asking women to draw their khimār over their bosoms.[14][15]
And say to the believing women that they should lower their gaze and guard their modesty; that they should not display their beauty and ornaments except what (must ordinarily) appear thereof; that they should draw their khimār over their breasts and not display their beauty except to their husband, their fathers, their husband's fathers, their sons, their husbands' sons, their brothers or their brothers' sons, or their sisters' sons, or their (Muslim) women, or the slaves whom their right hands possess, or male servants free of physical needs, or small children who have no sense of the shame of sex; and that they should not strike their feet in order to draw attention to their hidden ornaments. (Quran 24:31)In the following verse, the wives of Muhammad are asked to wear clothes (when they go out), as a measure to distinguish themselves from others, so that they are not harassed. Surah 33:59 reads:[15]
Those who harass believing men and believing women undeservedly, bear (on themselves) a calumny and a grievous sin. O Prophet! Enjoin your wives, your daughters, and the wives of true believers that they should cast their outer garments over their persons (when abroad): That is most convenient, that they may be distinguished and not be harassed. [...] (Quran 33:58–59)
Alternative views
Types of clothes worn by religious Shia Muslims in the greater Iranian region
Along with scriptural arguments, Leila Ahmed argues that head covering should not be compulsory in Islam because the veil predates the revelation of the Qur'an. Head-covering was introduced into Arabia long before Muhammad, primarily through Arab contacts with Syria and Iran, where the hijab was a sign of social status. After all, only a woman who need not work in the fields could afford to remain secluded and veiled.[11][17]
Ahmed argues for a more liberal approach to hijab. Among her arguments is that while some Qur'anic verses enjoin women in general to "draw their Jilbabs (overgarment or cloak) around them to be recognized as believers and so that no harm will come to them"[Quran 33:58–59] and "guard their private parts... and drape down khimar over their breasts [when in the presence of unrelated men]",[Quran 24:31] they urge modesty. The word "khimar" refers to a piece of cloth that covers the head, or headscarf.[18] While the term "hijab" was originally anything that was used to conceal,[19] it became used to refer to concealing garments worn by women outside the house, specifically the headscarf or khimar.[20]
Other verses do mention separation of men and women.
Abide still in your homes and make not a dazzling display like that of the former times of ignorance[Quran 33:32–33]
And when ye ask of them [the wives of the Prophet] anything, ask it of them from behind a curtain.[Quran 33:53]According to at least three authors (Karen Armstrong, Reza Aslan and Leila Ahmed), the stipulations of the hijab were originally meant only for Muhammad's wives, and were intended to maintain their inviolability. This was because Muhammad conducted all religious and civic affairs in the mosque adjacent to his home:
People were constantly coming in and out of this compound at all hours of the day. When delegations from other tribes came to speak with Prophet Muhammad, they would set up their tents for days at a time inside the open courtyard, just a few feet away from the apartments in which Prophet Muhammad's wives slept. And new emigrants who arrived in Yatrib would often stay within the mosque's walls until they could find suitable homes.[11]According to Ahmed:
By instituting seclusion Prophet Muhammad was creating a distance between his wives and this thronging community on their doorstep.[12]They argue that the term darabat al-hijab ("taking the veil"), was used synonymously and interchangeably with "becoming Prophet Muhammad's wife", and that during Muhammad's life, no other Muslim woman wore the hijab. Aslan suggests that Muslim women started to wear the hijab to emulate Muhammad's wives, who are revered as "Mothers of the Believers" in Islam,[11] and states "there was no tradition of veiling until around 627 C.E." in the Muslim community.[11][12]
Another interpretation differing from the traditional states that a veil is not compulsory in front of blind men and men lacking physical desire.[21][22][23]
Hadith
The Arabic word jilbab is translated as "cloak" in the following passage. Contemporary Salafis insist that the jilbab (which is worn over the Kimaar and covers from the head to the toe) worn today is the same garment mentioned in the Qur'an and the hadith; other translators have chosen to use less specific terms:- Narrated Anas ibn Malik: "I know (about) the Hijab (the order of veiling of women) more than anybody else. Ubay ibn Ka'b used to ask me about it. Allah's Apostle became the bridegroom of Zaynab bint Jahsh whom he married at Medina. After the sun had risen high in the sky, the Prophet invited the people to a meal. Allah's Apostle remained sitting and some people remained sitting with him after the other guests had left. Then Allah's Apostle got up and went away, and I too, followed him till he reached the door of 'Aisha's room. Then he thought that the people must have left the place by then, so he returned and I also returned with him. Behold, the people were still sitting at their places. So he went back again for the second time, and I went along with him too. When we reached the door of 'Aisha's room, he returned and I also returned with him to see that the people had left. Thereupon the Prophet hung a curtain between me and him and the Verse regarding the order for (veiling of women) Hijab was revealed." Sahih al-Bukhari, 7:65:375, Sahih Muslim, 8:3334
- Narrated Umm Salama Hind bint Abi Umayya, Ummul Mu'minin: "When the verse 'That they should cast their outer garments over their persons' was revealed, the women of Ansar came out as if they had crows hanging down over their heads by wearing outer garments." 32:4090. Abū Dawud classed this hadith as authentic.
- Narrated Safiya bint Shaiba: "Aisha used to say: 'When (the Verse): "They should draw their veils (Khumur) over their necks and bosoms (juyyub)," was revealed, (the ladies) cut their waist sheets at the edges and covered their faces with the cut pieces.'" Sahih al-Bukhari, 6:60:282, 32:4091.
Dress code required by hijab
Female art students in Afghanistan
Indonesian women in Hong Kong
Women
Detailed scholarly attention has focused on prescribing female dress in conformity with hijab. The four major Sunni schools of thought (Hanafi, Shafi'i, Maliki and Hanbali) hold that the entire body of the woman, except her face and hands – though a few clerics[who?] say face, hands – must be covered during prayer and in public settings (see Awrah). There are those who allow the feet to be uncovered as well as the hands and face.[25][26]It is recommended that women wear clothing that is not form fitting to the body: either modest forms of western clothing (long shirts and skirts), or the more traditional jilbāb, a high-necked, loose robe that covers the arms and legs. A khimār or shaylah, a scarf or cowl that covers all but the face, is also worn in many different styles. Some scholars encourage covering the face, while some follow the opinion that it is only not obligatory to cover the face and the hands but mustahab (Highly recommended). Other scholars oppose face covering, particularly in the West, where the woman may draw more attention as a result. These garments are very different in cut from most of the traditional forms of ħijāb, and they are worn worldwide by Muslims.
Many Muslim scholars believe that it is a basic requirement of Islamic law that women keep their hair and bodies covered in the presence of people of the opposite sex other than close family members (those close enough to be forbidden to marry—see mahram). These include the Iraqi Shia Marja' (Grand Ayatollah) Ali al-Sistani;[27] the Sunni Permanent Committee for Islamic Research and Issuing Fatwas in Saudi Arabia;[28] and others.[29] According to some interpretations, these requirements extend to non-Muslim women as well. Some believers go so far as to specify exactly which areas of the body must be covered. In some cases, this is everything but the eyes, but most require that women cover everything but the face and hands. In nearly all Muslim cultures, young girls are not required to wear a ħijāb. There is not a single agreed age when a woman should begin wearing a ħijāb—but in many Muslim cultures, puberty is the dividing line.
In private, and in the presence of close relatives (mahrams), rules on dress relax. However, in the presence of the husband, most scholars stress the importance of mutual freedom and pleasure of the husband and wife.[30]
Garments
The burqa (also spelled burka) is the garment that covers women most completely: either only the eyes are visible, or nothing at all. Originating in what is now Pakistan, it is more commonly associated with the Afghan chadri. Typically, a burqa is composed of many yards of light material pleated around a cap that fits over the top of the head, or a scarf over the face (save the eyes). This type of veil is cultural as limited to the people of that part of the world.It has become tradition that Muslims in general, and Salafis in particular, believe the Qur'an demands women wear the garments known today as jilbāb and khumūr (the khumūr must be worn underneath the jilbāb). However, Qur'an translators and commentators translate the Arabic into English words with a general meaning, such as veils, head-coverings and shawls.[31] Ghamidi argues that verses [Quran 24:30] teach etiquette for male and female interactions, where khumūr is mentioned in reference to the clothing of Arab women in the 7th century, but there is no command to actually wear them in any specific way. Hence he considers head-covering a preferable practice but not a directive of the sharia (law).[32]
Men
Although certain general standards are widely accepted, there has been little interest in narrowly prescribing what constitutes modest dress for Muslim men. Many scholars recommend that men should cover themselves from the navel to the knees.[33] It is also widely accepted that male clothes should not be tight-fitting or "glamorous".[33]According to some sources, Muslim men should not wear gold jewelry, silk clothing, or adornments that are considered feminine.[34][35]
Fadwa El Guindi, a prominent Islamic scholar, writes, “Confining the study of the veil, just like the study of women, to the domain of gender in lieu of society and culture narrows the scope in a way that limits cultural understanding and theoretical conceptualization”[citation needed]
Sartorial hijab as practiced
See also: List of types of sartorial hijab
In Iran, where wearing the hijab is legally required, women,
especially younger ones, have taken to wearing transparent and very
loosely worn hijabs.In Turkey, where the hijab was formerly banned in private and state universities and schools, 11% of women once wore it, though 60% wore traditional non-Islamic headscarves, figures of which are often confused with hijab.[36][37][38] However, the ban was lifted from universities in 2011, from government buildings in 2013,[39] and from schools in 2014.[40]
Historical and cultural explanations
History
The term hijab is never used in the Qur'an to describe an article of clothing.[41] The only verses in the Qur'an that specifically reference women’s clothing, are those promoting modesty, instructing women to guard their private parts and throw a scarf over their bosoms in the presence of men.[41] The contemporary understanding of the hijab dates back to Hadith when the “verse of the hijab” descended upon the community in 627 CE.[42] Now documented in Sura 33: 53 the verse states, “And when you ask [his wives] for something, ask them from behind a partition. That is purer for your hearts and their hearts”.[43] This verse, however, was not addressed to women in general, but exclusively to Muhammad’s wives. As Muhammad’s influence increased, he entertained more and more visitors in the mosque, which was then his home. Often, these visitors stayed the night only feet away from his wives’ apartments. It is commonly understood that this verse was intended to protect his wives from these strangers.[44] During Muhammad’s lifetime no other women in the Ummah (Muslim community) observed the hijab. Instead, the term for donning the veil, darabat al-hijab, was used interchangeably with “becoming Muhammad’s wife”.[45] As stated by Reza Aslan, “The veil was neither compulsory nor widely adopted until generations after Muhammad’s death, when a large body of male scriptural and legal scholars began using their religious and political authority to regain the dominance they had lost in society as a result of the Prophet’s egalitarian reforms”.[44] Other scholars point out that the Qur'an does not require women to wear veils; rather, it was a social habit picked up with the expansion of Islam. In fact, since it was impractical for working women to wear veils, "A veiled woman silently announced that her husband was rich enough to keep her idle."[46]
Young woman from Nablus in a hijab (ca. 1867-1885)
Pre-Islamic Veiling Practices
Veiling did not originate with the advent of Islam. Statuettes depicting veiled priestesses precede all three Abrahamic religions (Christianity, Judaism, and Islam), dating back as far as 2500 BCE.[47] Elite women in ancient Mesopotamia and in the Byzantine, Greek, and Persian empires wore the veil as a sign of respectability and high status.[48] In ancient Mesopotamia, Assyria had explicit sumptuary laws detailing which women must veil and which women must not, depending upon the woman’s class, rank, and occupation in society. Veiling was meant to “differentiate between ‘respectable’ women and those who were publicly available”.[48] Female slaves and unchaste women were explicitly forbidden to veil and suffered harsh penalties if they did so. Veiling was thus a marker of rank and exclusive lifestyle, subtly illustrating upper-class women’s privilege over women in lower classes in the Assyrian community.Strict seclusion and the veiling of matrons were in place in Roman and Byzantine society as well. Between 550 and 323 B.C.E, prior to Christianity, respectable women in classical Greek society were expected to seclude themselves and wear clothing that concealed them from the eyes of strange men.[49] These customs influenced the later Byzantine empire where proper conduct for girls entailed that they be neither seen nor heard outside their home. Like in Assyrian law, respectable women were expected to veil and low-class women were forbidden from partaking in the practice. In Classical Rome, the Emperor Augustus encouraged his citizens all around the Mediterranean to enter temples "capo velato" literally "with their heads veiled", by which he intended clothing that did not differ much from traditional Saudi clothing for men and women today. Augustus himself appeared like this in propaganda pictures and temple portraits (see the Ara Pacis temple in Rome). The Romans were embedded in a larger Mediterranean/Middle Eastern milieu with roots in Mesopotamia (Iraq) and Egypt, and they transmitted this legacy to both the eastern and western parts of the Roman Empire, which today constitute approximately the Muslim Mediterranean (and parts of the Middle East) and Europe.
By the 5th and 6th centuries, societies of the Mediterranean Middle East were dominated by Christian and some Jewish populations. At the inception of Christianity, Jewish women were veiling the head and face. In Judaic scripture, Genesis 24:65, Numbers 5:18 and Isaiah 47:2 are references in the Old Testament refer to a headcovering for women. Although there is no positive command for women to cover their heads in the Old Testament, there are non-canonical rabbinical writings on tzniut, meaning "modesty".[50]
There is also a tradition of Christian headcovering for women, rooted in 1 Corinthians 11:2–16 and supported by various early Church Fathers[51][52][53][54][55] Early Christian art shows women wearing headcoverings.[56] During the ensuing centuries, women wore headcoverings during the meetings of the church, but the style of the covering varied.[57] The practice of head-covering gradually disappeared from most churches over the course of the twentieth century, but still persists in the form of nuns "taking the veil," and many orders of nuns' religious habits resemble the chador, the full-body cloak that leaves only the face exposed, which is worn as a form of hijab by some women, particularly in Iran. Some think that the word habarah (a complex cloak and veil traditional in Egypt) itself derives from early Christian and Judaic religious vocabulary.”[58] Scholar Leila Ahmed argues that “Whatever the cultural source or sources, a fierce misogyny was a distinct ingredient of Mediterranean and eventually Christian thought in the centuries immediately preceding the rise of Islam.”[59]
During the period directly preceding the Muslim conquest in 640 CE, the Sassanids ruled in Mesopotamia. Customs of Persian royalty at the time of the first Persian conquest of Mesopotamia continued to be practiced and became even more elaborate under the Sassanids. In addition to acknowledging the monotheistic religion of Zoroastrianism among the upper classes, such customs included large harems of women and, of most note for this article, veiling. Some scholars postulate that the customs of veiling and seclusion of women in early Islam were assimilated from the conquered Persian and Byzantine societies and then later on they were viewed as appropriate expressions of Quranic norms and values.
Thus, successive invasions during the Muslim conquest led to some synthesis in the cultural practices of Greek, Persian, and Mesopotamian empires and the Semitic peoples of the regions.[58] Because Islam identified with the monotheistic religions of the conquered empires, the practice was adopted as an appropriate expression of Qur'anic ideals regarding modesty and piety.[60] Veiling gradually spread to upper-class Arab women, and eventually it became widespread among Muslim women in cities throughout the Middle East. It gradually spread among urban populations, becoming more pervasive under Ottoman rule as a mark of rank and exclusive lifestyle.[58] Women in rural areas were much slower to adopt veiling because the garments interfered with their work in the fields.[61]
The mid-twentieth century saw a resurgence of the hijab in Egypt after a long period of decline as a result of the westernization of Egypt under the rule of Gamal Abdel Nasser. The hijab, veil, often taken to mean suppression of the Islamic woman, began to symbolize a commitment to "the service of the Islamic call [to help] devastated families."[62] The veil became a liberating symbol of being an Islamic woman with a cause for social justice.
Overall, the hijab is meant to highlight the individual’s relationship with Allah. Many scholars[who?] believe that the hijab was a source of separation, in which to allow Muhammad’s wives to find oneness with Allah.
Contemporary context
A model displaying a fashionable hijab at "Moslema In Style Fashion Show" (show for Muslim women apparels)
Soon this movement expanded outside of the youth realm and became a more widespread Muslim practice. Women viewed this way of dress as a way to both publicly announce their religious beliefs as well as a way to simultaneously reject western influences of dress and culture that were prevalent at the time. Despite many criticisms of the practice of hijab being oppressive and detrimental to women’s equality,[64] many Muslim women view the way of dress to be a positive thing. It is seen as a way to avoid harassment and unwanted sexual advances in public and works to desexualize women in the public sphere in order to instead allow them to enjoy equal rights of complete legal, economic, and political status. This modesty was not only demonstrated by their chosen way of dress but also by their serious demeanor which worked to show their dedication to modesty and Islamic beliefs.[63]
Controversy erupted over the practice. Many people, both men and women from backgrounds of both Islamic and non-Islamic faith questioned the hijab and what it stood for in terms of women and their rights. There was questioning of whether in practice the hijab was truly a female choice or if women were being coerced or pressured into wearing it.[63] Many instances, such as a period of forced veiling for women in Iran, brought these issues to the forefront and generated great debate from both scholars and everyday people.
As the awakening movement gained momentum, its goals matured and shifted from promoting modesty and Islamic identity towards more of a political stance in terms of retaining support for Islamic nationalism and to resist western influences. Today the hijab means many different things for different people. For Islamic women who choose to wear the hijab it allows them to retain their modesty, morals and freedom of choice.[64] They choose to cover because they believe it is liberating and allows them to avoid harassment. Many people (both Muslim and non-Muslim) are against the wearing of the hijab and argue that the hijab causes issues with gender relations, works to silence and repress women both physically and metaphorically, and have many other problems with the practice. This difference in opinions has generated a plethora of discussion on the subject, both emotional and academic, which continues today.
Ever since September 11, 2001, the discussion and discourse on the hijab has intensified. Many nations have attempted to put restrictions on the hijab, which has led to a new wave of rebellion by women who instead turn to covering and wearing the hijab in even greater numbers.[64][66] Some of the more notable events that have occurred in the recent past can be read about in the further reading section.
Modern practice
Wearing the hijab in Kazakhstan is not prohibited, but is widely criticized as a foreign custom (the traditional scarf worn by Central Asian married women resemble the bandana, not the hijab), because it was not practiced until the fall of the USSR and the arrival of foreign Islamic missionaries.Governmental enforcement and bans
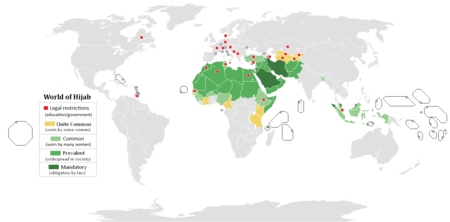
A map showing the prevalence of the Hijab
Some Muslims believe hijab covering for women should be compulsory as part of sharia, i.e. Muslim law. Wearing of the hijab was enforced by the Taliban regime in Afghanistan. The Taliban's Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan required women to cover not only their head but their face as well, because "the face of a woman is a source of corruption" for men not related to them.[67] Today, covering face by niqab is compulsory in many sacred places in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia.
Turkey, Tunisia, and Tajikistan are Muslim-majority countries where the law prohibits the wearing of hijab in government buildings, schools, and universities. In Tunisia, women were banned from wearing hijab in state offices in 1981 and in the 1980s and 1990s more restrictions were put in place.[68] In 2008 the Turkish government attempted to lift a ban on Muslim headscarves at universities, but were overturned by the country's Constitutional Court.[69] Though in December 2010, the Turkish government ended the headscarf ban in universities.[70]
Iran went from banning hijab in 1936 to making it compulsory in 1979. The tradition of veiling hair in Iranian culture has ancient pre-Islamic origins,[71] but the widespread custom was forcibly ended by Reza Shah's regime in 1936, as it was incompatible with his modernizing ambitions. The police arrested women who wore the veil and would forcibly remove it, and these policies outraged the Shi'a clerics, and ordinary men and women, to whom appearing in public without their cover was tantamount to nakedness. Many women refused to leave the house out of fear of being assaulted by Reza Shah's police.[72] Eventually rules of dress code were relaxed, and after Reza Shah's abdication in 1941 the compulsory element in the policy of unveiling was abandoned. According to Mohammad Reza Shah Pahlavi, between 1941 and 1979, wearing hejab [hijab] was no longer offensive, but still considered it to be a real hindrance to climbing the social ladder, a badge of backwardness and a marker of class. A headscarf, let alone the chador, prejudiced the chances of advancement in work and society not only of working women but also of men, who were increasingly expected to appear with their wives at social functions. At the time of the overthrow of the Shah's regime after Iranian Revolution of 1979, Ayatollah Ruhollah Khomeini made a speech on the first International Women's Day declaring that women should wear the veil in state ministries.[73][74] This led to widespread demonstrations in March of 1979 by women all across the country by women opposed to the imposition of the veil.[73][74] However, legally-imposed veiling gradually took hold: women not covering their hair and body in hijab were first denied the right to enter governmental institutions and facilities, and hijab ultimately became universally mandatory in 1984.[74] Under Penal Code provisions, women who refuse to wear the prescribed hijab will be sentenced to 72 lashes.[74]
Some Iranian women wear their headscarves far back on their heads revealing most of their hair. More conservative types of hijab like kimars and chadors are still widespread in government institutions, mosques, sacred places and conservative areas.
On March 15, 2004, France passed a law banning "symbols or clothes through which students conspicuously display their religious affiliation" in public primary schools, middle schools, and secondary schools. In the Belgian city of Maaseik, Niqāb has been banned since 2006.[75] On July 13, 2010, France's lower house of parliament overwhelmingly approved a bill that would ban wearing the Islamic full veil in public. There were 335 votes for the bill and one against in the 557-seat National Assembly.
In 2014 the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant was reported to have executed several women for not wearing niqab with gloves.[76]
In 2014 the Aceh Legislative Council passed Qanun Acara Jinayat (a sharia-based criminal procedures code) applying Islamic law to everyone in the province, including non-Muslims. This would compel non-Muslims to wear hijab. The bill is under national government review.[77]
Non-governmental enforcement
See also: Islamization of the Gaza Strip
Non-governmental enforcement of hijab is found in many parts of the Muslim world.Successful informal coercion of women by sectors of society to wear hijab has been reported in Gaza where Mujama' al-Islami, the predecessor of Hamas, reportedly used "a mixture of consent and coercion" to "'restore' hijab" on urban educated women in Gaza in the late 1970s and 1980s.[78]
Similar behaviour was displayed by Hamas itself during the First Intifada in Palestine. Though a relatively small movement at this time, Hamas exploited the political vacuum left by perceived failures in strategy by the Palestinian factions to call for a 'return' to Islam as a path to success, a campaign that focused on the role of women.[79] Hamas campaigned for the wearing of the hijab alongside other measures, including insisting women stay at home, segregation from men and the promotion of polygamy. In the course of this campaign women who chose not to wear the hijab were verbally and physically harassed, with the result that the hijab was being worn 'just to avoid problems on the streets'.[80]
In Srinagar, India in 2001 an "acid attack on four young Muslim women ... by an unknown militant outfit [was followed by] swift compliance by women of all ages on the issue of wearing the chadar (head-dress) in public."[81][82][83]
Radicals in Gaza have been accused of attacking or threatening to attack the faces of women in an effort to intimidate them from wearing allegedly immodest dress.[84]








Tidak ada komentar:
Posting Komentar